In today’s digital age, mobile apps are pivotal in driving innovation and operational efficiency across various sectors, including those that are highly regulated like healthcare, finance, and legal. However, developing apps for these industries comes with its unique challenges, primarily due to the stringent regulatory standards these sectors must adhere to. This blog post explores the essential design principles necessary for creating effective and compliant mobile apps in highly regulated industries.
Introduction

Mobile technology has profoundly transformed business operations and customer interactions in nearly every industry. That’s why we at Grafitis pay attention to mobile optimization. However, when it comes to regulated sectors, app developers must navigate a complex landscape of legal requirements and security measures. Adhering to these regulations is crucial not only for legal compliance but also to maintain trust and protect sensitive information.
Understanding Regulatory Requirements
Key Regulations to Consider
- Healthcare: Apps dealing with health information must comply with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the U.S., which safeguards the privacy and security of patient data.
- Finance: Financial apps are subject to regulations like SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act) and GLBA (Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act) in the U.S., or GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the EU, which focus on the integrity and security of financial data and personal information.
- Legal: Legal apps must ensure data protection and confidentiality in line with standards such as the Data Protection Act 2018 in the UK, or various state-specific laws in the U.S.
Developers must have a thorough understanding of these regulations to ensure their mobile app designs do not inadvertently violate legal standards.
Core Design Principles
1. Security First
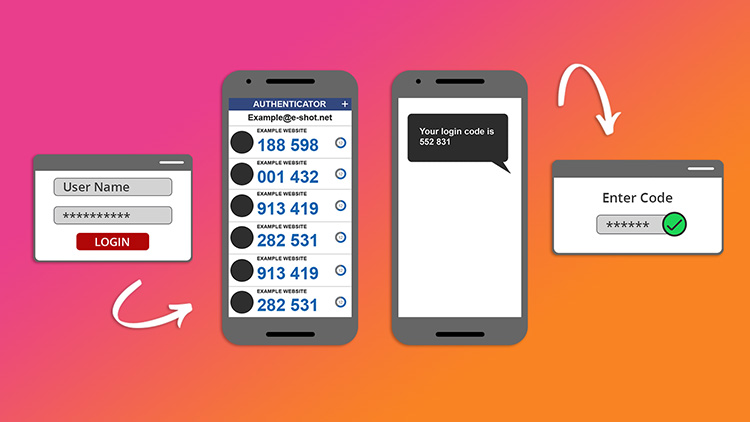
In highly regulated industries, security is not an afterthought but a foundation of app design. Apps must incorporate robust security measures like encryption, secure data storage, and secure data transmission. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometric security features can also enhance access controls, ensuring that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized users.
2. Privacy by Design
Adopting a privacy by design approach means integrating privacy into the software development process from the ground up. This involves minimizing data collection to what’s absolutely necessary, securing consent where needed, and enabling users to easily access, correct, and delete their personal information.
3. Simplicity and Clarity
User interface (UI) design in regulated industries should focus on simplicity and clarity to avoid user errors that could lead to data breaches or other security issues. This includes using clear, jargon-free language, intuitive navigation, and straightforward layouts that guide the user naturally through the app’s functionalities.
4. Accessibility
Accessibility ensures that apps are usable by people with various disabilities, including visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments. This not only broadens the user base but is also a legal requirement in many regions. Implementing voice commands, screen readers, and large text options can make the app more accessible.
5. Audit Trails
Creating audit trails involves keeping detailed logs of user activities within the app. This is crucial for compliance in regulated industries, as it provides a way to track and verify that all actions meet regulatory standards and can be crucial during audits or investigations.
6. Continuous Compliance

Regulatory landscapes are constantly evolving, and mobile apps must be designed to accommodate these changes. This means implementing a flexible architecture that can adapt to new regulations quickly and cost-effectively.
Best Practices in Development
Collaborate with Legal Experts
Regular collaboration between developers and legal experts is essential to align the app’s design and functionality with current laws and regulations. This collaborative approach ensures that the app remains compliant at every stage of its lifecycle.
User Testing

User testing is particularly important in regulated industries to ensure that the app not only meets user expectations but also adheres to regulatory requirements. This should include testing for usability, security, and compliance across various user demographics.
Scalability
Designing with scalability in mind allows the app to handle increasing amounts of data and growing numbers of users without compromising performance or security. This is particularly important in industries like healthcare and finance, where data volumes can grow exponentially.
Conclusion
Developing mobile apps for highly regulated industries requires a careful, meticulous approach that integrates security, privacy, and compliance into every facet of the app design and development process. By adhering to these design principles, developers can not only ensure regulatory compliance but also provide users with a secure, efficient, and user-friendly experience.


